Generative AI Use Cases for Employees in the Workplace
The advent of generative AI technology is an invaluable asset for businesses aiming to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world, aiding in tasks from drafting personalized marketing content to designing product prototypes. Its incorporation in companies calls for employees to anticipate its day-to-day impact and take charge of this technology—capturing its value to create value in and out the workplace.
“Current generative AI and other technologies have the potential to automate work activities that absorb 60 to 70 percent of employees’ time today.”—McKinsey & Company
The following read covers the economic outlook and key impact areas of generative AI in the corporate workplace, along with five specific use cases pertinent to employees.
What's Inside
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is an innovative technology that leverages advanced machine learning models to generate new content— including text, images, music, and more—with a level of quality that mimics, if not surpasses, human creativity. This technology is transforming various industries by automating creative processes and boosting productivity.
Economic Outlook and Workplace Impact Areas of Generative AI
It is known that AI technologies can contribute towards simple tasks that employees perform daily. However, new research shows generative AI may also impact knowledge work—those activities that involve decision making and collaboration, which previously had the lowest potential for automation (McKinsey & Company).
Examples of knowledge work with the potential for automation include applying expertise, supervising, managing, developing talent, creating documentation, and interfacing with clients and other stakeholders.
There is a positive outlook for generative AI in the corporate workplace, key forecasts including a labor productivity boost and significant labor cost savings. According to McKinsey & Company, “the total [global] economic benefits of generative AI—including the major use cases explored and the myriad increases in productivity that are likely to materialize when the technology is applied across knowledge workers’ activities—amounts to $6.1 trillion to $7.9 trillion annually.”
Yet, slow progress persists due to underdeveloped regulation and stymied integration efforts. A Q2 insights report published by Deloitte found that “the percentage of organizations reporting they were already achieving their expected benefits to a ‘large’ or ‘very large’ extent is 18%–36%, depending on the type of benefit being pursued. While not a high percentage, the statistic underscores companies' investments in the technology and their objective of integrating generative AI. Though mainstream generative AI adoption in the workplace is on the horizon, it remains a distant horizon.
Use Cases of Generative AI in the Corporate Workplace
At a larger scale, generative AI has the potential to optimize company operations and fuel economic growth. For the employee, the integration of generative AI introduces a plethora of beneficial use cases, including automated tasks, client collaboration, data fusion, knowledge management applications, and personalized employee feedback and training.
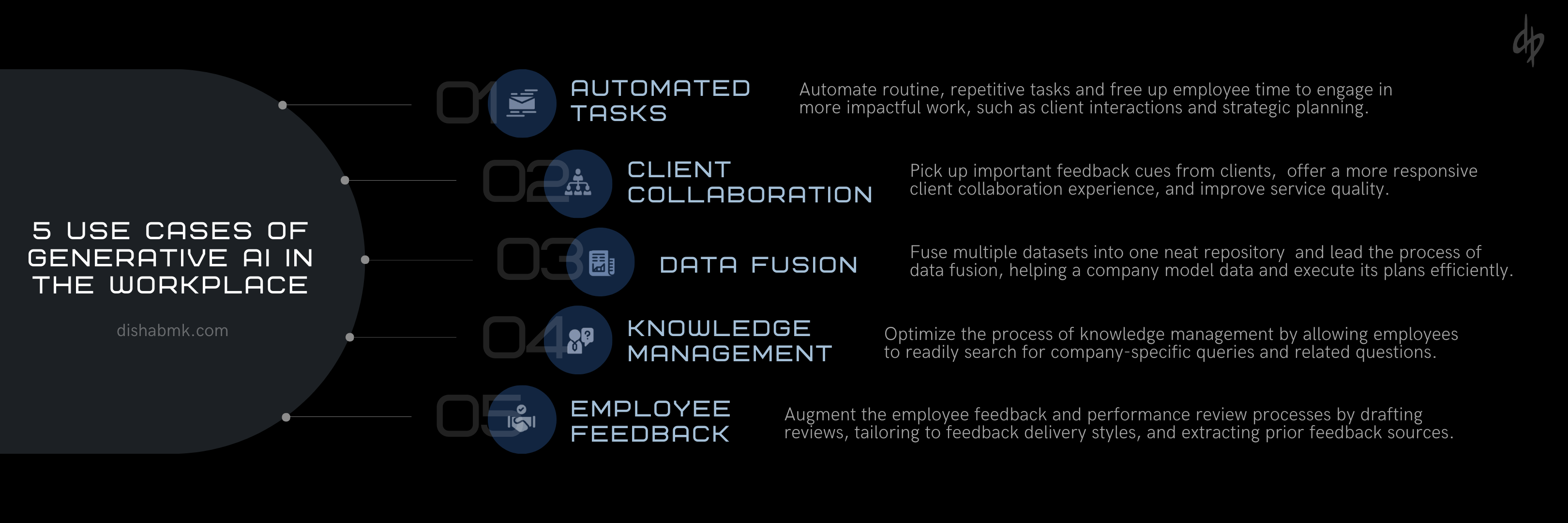
Automated Tasks
Generative AI is set to transform the workplace by automating routine, repetitive tasks. This innovation would free up employee time to engage in more impactful work, such as client interactions and strategic planning.
“It may soon be standard practice, for example, for such systems to craft most or all of our written or image-based content–to provide first drafts of emails, letters, articles, computer programs, reports, blog posts, presentations, videos, and so forth” (hbr.org)
A significant aspect of corporate work involves using key workflow tools, such as Microsoft Office (Outlook, Teams, Excel, OneNote, PowerPoint), Slack, and Google apps (Gmail, Sheets, Docs, Slides). As generative AI evolves within companies, its ability to facilitate cross-communication between apps will further streamline operations and boost productivity.
For employees, this may mean spending fewer hours creating organized Excel layouts and formulating detailed Excel functions—since AI will take care of generating optimal worksheet designs and effective formulas. Instead, employees can hone their expertise on analyzing trends and drawing conclusions from the workbook’s data.
Or, consider an employee at "Company X" who receives a ping from a coworker on Teams, asking them to email "Manager Y" about "Z information." Generative AI can pick up on the task and draft a ready-to-send email for the employee by integrating Teams and Outlook. In this scenario, an Outlook pop-up could appear immediately upon receiving the Teams message, containing an editable email draft addressed to "ManagerY@CompanyX.com" with the body: "Hello Y, I wanted to reach out regarding Z information. Please let me know if you have any questions. Many thanks, [Employee Name]." As the volume and complexity of emails increase, the convenience of simply hitting "send" upon reviewing the AI-generated email becomes both time-efficient and appealing.
Client Collaboration
A large, and perhaps the greatest, responsibility held by employees is providing value to their clients—not only meeting, but exceeding, expectations, communicating thoroughly, and representing their company well in the process. Generative AI can help strengthen this dynamic by picking up important feedback cues from clients and offering a more responsive client collaboration experience.
An important aspect of generative AI is its ability to draft highly personalized responses to each client comment and identify which departments to notify as part of the workflow. For instance, consider a scenario where a client hires a third-party consulting firm for accounting services and provides feedback, noting the service isn’t a job well done. The AI platform can summarize the situation, determine the relevant departments—such as Human Resources for addressing any employee-related concerns, IT for technical issues with the accounting software, and the consulting team for service quality—and automate notifications to each accordingly. Thus, generative AI can provide a holistic view of the client's feedback and foster cross-department collaboration for swifter, more coordinated responses to client needs.
“GenAI systems also enable a breakthrough in sentiment analysis — or distinguishing positive, neutral, and negative customer sentiments… sarcasm, humor, and other subtleties of customer expression. (A hotel chain’s sentiment analysis system, for example, couldn’t determine whether ‘the pool was too cool’ was a positive or negative sentiment.) But researchers have found that GenAI models can have precision levels of over 95%, can accurately assess sentiment in multiple languages, and can identify nuanced feelings such as nostalgia and loyalty” (hbr.org).
Generative AI can improve service quality itself. Continuing with the example of accounting consulting firms, the technology can create comprehensive client profiles from various data sources. It can also consolidate and analyze client financial data, past interactions, and individual accounting needs, enabling consulting teams to execute their engagements in a more targeted and strategic manner.
Furthermore, generative AI can ease the back-and-forth communication with clients, allowing employees to focus on delivering the requested work. For example, employees use Excel trackers or other software to track progress internally. When integrated with AI, this information can be relayed to clients whenever prompted—providing summarized, on-demand project status updates; Indeed, a Forbes article mentions how “these tools give customers [and clients] 24/7 access to support, 365 days a year, via multiple channels… Plus, this can be done in multiple languages.”



AI-generated renders of client collaboration with AI platforms.
Data Fusion
To serve clients better, companies will often leverage a combination of internal and public data through a practice known as data fusion.
Generative AI can fuse multiple datasets into one neat repository, thereby capable of leading the process of data fusion—an otherwise intricate, lengthy task for employees.
However, companies are still tasked with overcoming low quality data. To tap into generative AI’s potential in data fusion, it would require employees to prepare clean, ready-to-go data to input into AI systems; “success with genAI ‘hinges on high-quality, “business-ready” data, which is guided by a robust data foundation, data governance, and standards’” (hbr.org). Once accomplished, AI’s ability to model data and execute a company’s plan drastically increases.
”Data is the lifeblood of AI, but if left unchecked, it can quickly become a deterrent.”—S&P Global
Knowledge Management Applications
Generative AI platforms like ChatGPT leverage vast amounts of web-based information. Companies can develop their own AI platforms, utilizing internal knowledge as the primary source of informatiom. With generative AI, employees can readily search for related questions or company-specific queries, optimizing the process of knowledge management.
Generative AI is not confined to conventional company knowledge and documentation. Its power lies in extracting and relaying insights from unique sources, thereby establishing the potency of introducing this technology to knowledge management; AI can “help organizations draw out previously unknown connections and insights from sources such as phone transcripts, emails, chats and CRM systems…Each day, every employee could be greeted with a specially curated summary of the news, events and action items that they need to see” (forbes.com).
Certain companies have already recognized the opportunity and are integrating generative AI in KM; “Morgan Stanley, for example, is working with OpenAI’s GPT-3 to fine-tune training on wealth management content, so that financial advisors can both search for existing knowledge within the firm and create tailored content for clients easily” (hbr.org).
Personalized Employee Feedback and Training
Employee feedback and performance reviews are undeniably interpersonal processes. Maintaining the human aspect is necessary and irreplaceable. Nevertheless, generative AI can augment these processes by automating the drafting of reviews, tailoring to feedback delivery styles, and gathering previously overlooked sources of information to better represent employees during feedback.
“Generative AI can save managers time… by collecting things like peer- or customer-generated performance data… That might include the kudos people receive in Slack channels or email conversations about their work performance as well as comments about skill areas where they need to improve… GenAI can scrape your internal data and put together good performance summaries for managers to review” (shrm.org).
It’s important to note employees differ in their preferred style of performance feedback delivery. While some benefit from direct bottom-line advice, others respond to criticism better when offered more constructively and positively. Here, AI can craft feedback that is empathetic and fine-tuned to each employee’s needs. Where one manager may label an employee as "unreliable," AI might provide less ambiguous language and offer specifics—like improve timely delivery of tasks or provide more frequent project status updates to superiors.



AI-generated abstract images of employee feedback platforms.
Managers and other review-providers can also reap benefits from generative AI integration; with AI drafting initial performance reviews, managers can focus on refining their observations and dedicating more time to one-on-one discussions with employees.
Moreover, the technology can recall feedback to enhance an employee’s training initiatives; “gen AI can analyze an individual employee's learning style, performance data, and career development goals to generate customized learning modules, activities, and educational materials” (forbes.com). To highlight this point, consider a somewhat shy customer service representative: generative AI may provide customer interaction suggestions from the employee’s records of complaints received on calls and previous remedial actions, walking through each step and offering personalized areas of improvement—such as maintaining a steady tone and pace—to build the employee’s confidence on calls.
Conclusion—A Note to Employees
With the integration of generative AI in the workplace soon to be materialized and widespread, both awe and preparedness for the technology are commanded.
The conveniences that generative AI will deliver must be balanced with the changes it will bring to the workplace. The first step towards preparedness involves employees actively learning its usage and responsibilities. Employees are accountable for training generative AI platforms as they see usage increase within their companies. For instance, though generative AI may help contribute towards data fusion, employees will still serve an active role in the oversight of data inputted—controlling both the quality and selection per company guidelines.
As part of a company, employees work together—power in number—to positively impact clients and enact change. With generative AI, employees may be leaders in their own realm by leading this upcoming wave whilst tapping into its potential for numerous work use cases. Generative AI is proving to be boundless in its innovative abilities, but so is the ever-expanding scope of employees with AI integration.
Employees are pioneering the next technological era, often without realizing it. With each use, they shape generative AI, and they shape its place in the future.
References and Credits
- Chui, Michael, et al. “The Economic Potential of Generative AI: The Next Productivity Frontier.” McKinsey & Company, McKinsey & Company, 14 June 2023.
- Hamirani, Q. “Here’s How Generative AI Will Redefine the Workplace.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 2 July 2024.
- Immerman, David, and Nick Patience. “2023 Global Trends in AI.” WEKA, 19 Dec. 2023.
- Marr, Bernard. “How Generative AI Is Revolutionizing Customer Service.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 2 July 2024.
- Mittal, Nitin, and Thomas H. Davenport. “How Generative AI Is Changing Creative Work.” Harvard Business Review, 15 Aug. 2023.
- Ojansuu, Perttu. “Knowledge Management Is Broken: Here’s How Generative AI Could Fix It.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 7 Dec. 2023.
- “State of Generative AI in the Enterprise 2024.” Deloitte, Accessed 6 July 2024.
- Thompson, Michael E., et al. “GenAI Can Help Companies Do More with Customer Feedback.” Harvard Business Review, 30 Apr. 2024.
- Tiwari, Priyanka, and Thomas H. Davenport. “Is Your Company’s Data Ready for Generative AI?” Harvard Business Review, 26 Mar. 2024.
- Zielinski, Dave. “How HR Is Using Generative AI in Performance Management.” SHRM, 28 Dec. 2023.

